NAVLIPI
World’s first practical phonemic (also phonetic) alphabet, based on Latin alphabet. See: https://navlipi.org
All languages
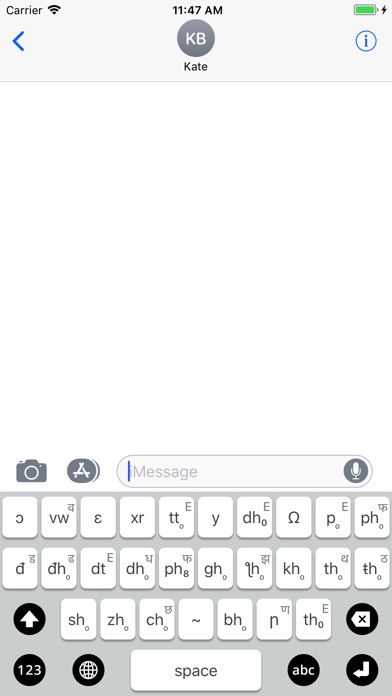
Superscripts on some keys: E (English); M (Mandarin); T (Tamil); A (Arabic); Dewanaagari letter.
Long vowels by reduplication: Short i, u -> Long ii, uu, etc; aa an exception.
Common vowels
• aa English father, Hindi आ
• Ω English ball, vowel in Hindi कौन
• ɔ (inverted-c) English Jack, vowel in Hindi मै
• q English about, 2nd vowel in Hindi यन्त्र
• a English but, Hindi अ
• e English bet; ee fair, vowel in Hindi है; ε English gray, Hindi ए, Spanish que
• y French tu, German ȕber; o// feuille; o/ German schön
Common non-vowels (consonants)
• j English yes, Hindi य
• ƪ (inverted-j) English Jack, Hindi ज
• c Spanish chica, Hindi च
• Aspiration (महाप्राण): Add hₒ to letter being aspirated. Thus, k (Hindi क), p (Hindi प) to khₒ (ख), phₒ (फ)
• Fricatization (hissing sound): Add h₀. Except: x for velar unvoiced fricative (Scots loch, Hindi/Faarsi ख्वाब)
• ƹ for voiced velar fricative, Hindi/Faarsi ग.म
• sh₀ English shoot, Hindi श; zh₀ English pleasure
Nasals
• As tilde symbol (~), or with n₀₀, m₀₀; place after syllable. Thus, Hindi हाां, French mon, Portuguese Saõ -> haa~ (haan₀₀), mo~ (mon₀₀), Saao~ (Saaon₀₀)
• Velar, nasals nₒ (Dewanaagari ङ, English king -> kinₒg); palatal η (Dewanaagari ञ, English inch iηc)
Upper-, lower- case letters ARE distinguished.
Specific languages
English, West European, Russian languages
• Alveolar t- , d as ŧŧ (or just tt ), đt (or just dt)
• Unvoiced, voiced dental fricatives: English thin -> th₀in, this -> dh₀is
Hindi, other Indian languages
• Retroflex (मूर्धन्त्य) non-vowels (ट, ठ, ड, ढ, ण) ŧ, ŧhₒ, đ, đhₒ, n
• Flaps add dot (.). Thus ट. ड. ण. become ŧ. đ. n.
• Vowel r-sound (ऋ): ȓ
• Wisarga: as colon (:)
• Diphthongs ऐ, औ, if actual diphthongs: aaε, aau. But these frequently pronounced as vowels ( cf. मै, है, कौन )
• Retroflex Tamil l-like sound (zh in Latin transcription) as r
Arabic
• Unvoiced uvular k-sound (q in Latin transcription): k..
• Pharyngealized (faucal) dental t-, d- as t.., d..
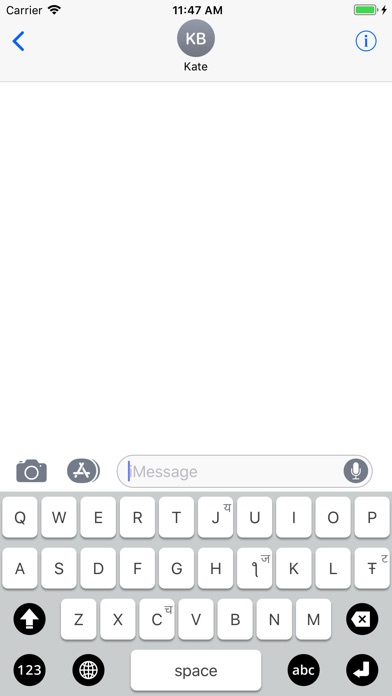
Mandarin
• 4 standard tones: leftmost 4 keys in top row of 3rd Navlipi keyboard. Placed after syllable having tone
• hs-sound (x in Latin transcription, Xie Xie, “thank you”): ŧŧh₀
Select African languages
• “Velarized” bilabials kp, gb
• Initial nasals as n₀₀, m₀₀. E.g. Ngoma, Mbeki as N₀₀gomaa, M₀₀bƐki
Phonemic renditions
Hindi
• vw for both v, w sounds in Hindi
• f, ph-sounds, jointly as ph₈
English
• pₒ for both p and ph (aspirated-p)
• ttₒ for alveolar t, th-sounds
Standard French, Hochdeutsch
• xr for both “throaty-r”, “rolled-r”
Mandarin
• Both p-, b-sounds, as b∞
• Both alveolar t, d-sounds as d∞
Tamil
• Both dental t, th sounds as tₒ